[toc]
Pinia笔记
Pinia官网:https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/
什么是Pinia?
Pinia 是 Vue 的最新状态管理库 ,是 Vuex 状态管理库的替代品。
手动添加Pinia到Vue3工程中
Pinia可以在工程创建时自动添加,也可以工程创建完毕后手动添加到工程中。
- 首先安装Pinia
# yarn 包管理器
yarn add pinia
# npm 包管理器
npm install pinia- 创建一个空的Vue3工程
npm init vue@latest- 修改工程的main.js文件,引入pinia
//引入样式文件
import './assets/main.css'
//引入createApp和createPinia函数
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
//引入根组件App.vue
import App from './App.vue'
//创建根组件App.vue的实例对象app
const app = createApp(App)
//创建实例对象pinia
const pinia = createPinia()
//将根组件实例对象app与实例对象pinia产生关联
app.use(pinia)
//将根组件实例对象app挂载到index.html中id=app的标签下
app.mount('#app')- 以上就将Pinia添加到前端工程中了。
Pinia基础使用
核心概念:Store 仓库
仓库 Store 是一个保存状态和业务逻辑的实体,它并不与组件树绑定。它承载着全局状态,每个组件都可以读取和写入它。
Store有三个子概念,state、getter 和 action。这些子概念相当于组件中的 data、 computed 和 methods。
什么时候使用 Store?
- 一个Store应该包含可以在整个应用中访问的公共数据。例如显示在导航栏中的用户信息。
- 另外,应该避免在Store中引入那些可以在组件中保存的本地数据。
如何使用 Store?
例如我们想在整个应用中,创建一个用户信息store。
① 在工程中的src目录下创建store目录,并且在目录中创建userStore.js文件
- store目录主要存放整个应用中的所有仓库文件
- userStore.js文件用来存储和管理全局用户信息的。
② 在userStore.js文件中创建用户信息store对象。
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
// 通过defineStore,你可以创建一个store仓库对象。
// store仓库对象的名字,最好以`use`开头且以`Store`结尾。(比如 `useUserStore`,`useCartStore`)
// 第一个参数是你的整个应用中 Store 的唯一 ID。
// 第二个参数是Setup 函数
export const useUserStore = defineStore('userStore', ()=>{
// 仓库的其他配置...
})- id是必须传入的。建议将defineStore()返回的函数命名为 use...
- defineStore() 的第二个参数可接受两类值:Setup 函数或 Option 对象。
③ 完整例子
- 定义store
- 组件使用store
userStore.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
//defineStore() 的第二个参数传入Setup函数
//在Setup函数可以使用vue3的组合式API
export const useUserStore = defineStore('userStore',()=>{
// 定义数据。ref()响应式对象 就是 state 属性
const age = ref(10)
// 定义数据的计算属性。computed() 就是 getters
const age2 = computed(()=> age.value * 2)
// 定义操作数据的方法。function() 就是 actions
function addAge() {
age.value ++
}
//将数据和方法 return出去
return { age, addAge, age2 }
})defineStore的第二个参数可以传入setup函数。在这个setup函数中
- ref() 就是 state
- computed() 就是 getters
- function() 就是 actions
HelloWorld.vue
<script setup>
//引入useUserStore
import { useUserStore } from '@/store/userStore'
//执行useUserStore函数,获取仓库对象实例
const userStore = useUserStore()
</script>
<!--在模板组件中使用state数据和actions方法和计算属性。-->
<template>
user age is {{ userStore.age }} - {{ userStore.age2 }}
<button @click="userStore.addAge">button1</button>
</template>state
如果说store是仓库,那么state就是仓库中存储的数据了。
defineStore的第二个参数可以传入setup函数。在这个setup函数中 ref()返回的响应式对象就是 state 数据。
在store中定义state数据
useUserStore.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref } from 'vue'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('userStore',()=>{
// 定义state数据 user
const count = ref(0)
const user = ref({ id:10,name:"xiaoming",age:10})
//将数据 return 出去
return { user,count }
})在组件中操作state数据
Hello.vue
<script setup>
//引入useUserStore
import { useUserStore } from '@/store/userStore'
//执行useUserStore函数,获取仓库对象实例
const userStore = useUserStore()
</script>
<!--在模板组件中使用state数据和actions方法和计算属性。-->
<template>
user is {{ userStore.user }}
count is {{ userStore.count }}
</template>一般可以通过store对象实例直接修改state数据。但是对于全局数据,不建议直接修改。而是应该通过store中设置的函数来修改state数据。
getter
store是仓库,state是仓库中的数据。那么getter就是对state数据的计算属性值。
defineStore的第二个参数可以传入setup函数。在这个setup函数中computed() 就是 getter。
例子如下
在store中定义state数据和Getter计算属性
useUserStore.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref } from 'vue'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('userStore',()=>{
// 定义state数据 user
const count = ref(0)
const count2 = computed(()=> count.value * 2)
//将数据 return 出去
return { count2,count }
})在组件中操作state数据和getters计算属性
Hello.vue
<script setup>
//引入useUserStore
import { useUserStore } from '@/store/userStore'
//执行useUserStore函数,获取仓库对象实例
const userStore = useUserStore()
</script>
<!--在模板组件中使用state数据和actions方法和计算属性。-->
<template>
count is {{ userStore.count }}
count2 is {{ userStore.count2 }}
</template>action
store是仓库,state是仓库中的数据,getter是计算属性值。那么action就是修改state数据的方法。
defineStore的第二个参数可以传入setup函数。在这个setup函数中function() 就是 actions
例子
userStore.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('userStore',()=>{
const age = ref(10)
// 定义操作数据的方法。function() 就是 actions
function addAge() {
age.value ++
}
//将数据和方法 return出去
return { age, addAge}
})HelloWorld.vue
<script setup>
//引入useUserStore
import { useUserStore } from '@/store/userStore'
//执行useUserStore函数,获取仓库对象实例
const userStore = useUserStore()
</script>
<!--在模板组件中使用state数据和actions方法和计算属性。-->
<template>
user age is {{ userStore.age }}
<button @click="userStore.addAge">button1</button>
</template>action的异步实现
action可以是异步的,你可以在它们里面 await 调用任何 API,以及其他 action。
例子
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('userStore',()=>{
const ageList = ref([])
// 异步实现
// 通过axios来请求接口,异步给ageList赋值
const getAge = async() => {
const a = await axios.get("http://xxxxxx")
ageList.value = a
console.log(a)
}
//将数据和方法 return出去
return { ageList, getAge}
})Pinia持久化
pinia 和 vuex 一样,数据是短时的。只要一刷新页面,数据就会恢复成初始状态。为了避免这个问题,可以对其采用持久化保存方法。
持久化保存的原理是在 pinia 中对数据更新时,同步保存到 localStorage 或 sessionStorage 中,刷新页面后从本地存储中读取数据写入到pinia的store中。
推荐使用插件去实现持久化存储,这样更便捷,省时省力。推荐插件为pinia-plugin-persistedstate
- 安装pinia-plugin-persistedstate插件
npm i pinia-plugin-persistedstate
## 或者
yarn add pinia-plugin-persistedstate- 将插件添加到 pinia 实例上
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
const pinia = createPinia()
pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate)- 创建 Store时,在defineStore函数的第三个参数上设置persist选项为true
组合式写法
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref } from 'vue'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('userStore',()=>{
// 定义state数据 user
const user = ref({ id:10,name:"xiaoming",age:10})
function addAge() {
user.value.age ++
}
//return 出去
return { user,addAge }
},{
persist: true
})<script setup>
import { useUserStore } from '@/store/userStore'
const userStore = useUserStore()
</script>
<template>
user is {{ userStore.user }}
<button @click="userStore.addAge">add-Age</button>
</template>- 重启工程,此时pinia持久化就会生效。
- 当我们对store中的数据进行更新的时候,pinia会将更新的数据保存在 localStorage 中。然后刷新页面的时候,将 localStorage 中的数据写入到store中。
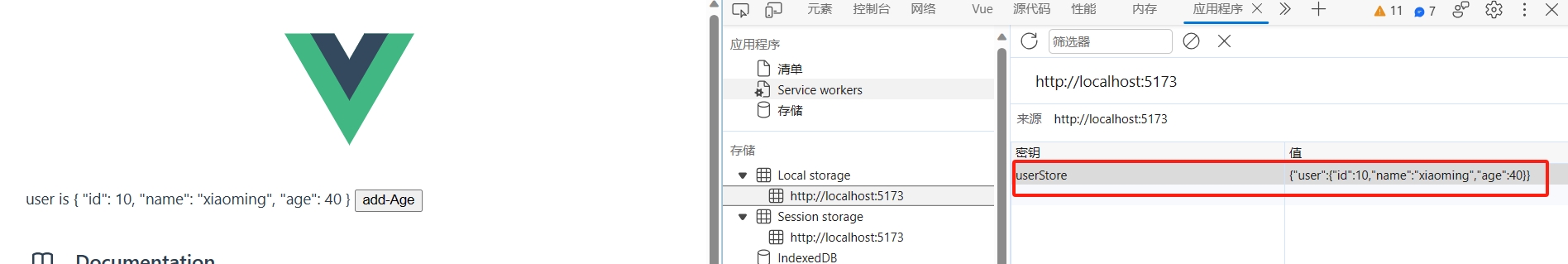
注意:localStorage中的数据的key是defineStore函数的第一个参数,即id值。
配置
如何你不想使用默认的配置,那么你可以将一个对象传递给 Store 的 persist 属性来进行自定义配置持久化。
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref } from 'vue'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('userStore',()=>{
// 定义state数据 user
const user = ref({ id:10,name:"xiaoming",age:10})
function addAge() {
user.value.age ++
}
//return 出去
return { user,addAge }
},{
persist: {
//这里进行自定义配置持久化
key: 'my-user-key',
storage: localStorage,
paths: ['user.id', 'user.name']
}
})- key 设置本地缓存数据的key。默认是defineStore的第一个参数。
- storage 设置本地缓存数据存储的位置。默认是localStorage。
- paths 可以设置state 中哪些数据需要被持久化。默认是所有state数据都持久化。
其余配置参考官网文档。
