[toc]
Python使用SQLite3库笔记
Python2.5以上的版本,都内置了SQLite3库。通过SQLite3库,python可以很方便的使用SQLite数据库。
使用SQLite3数据的步骤过程
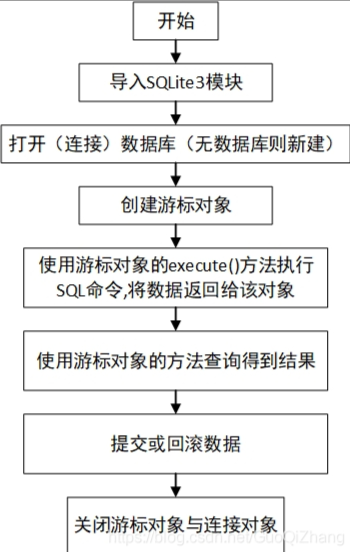
- 查询操作不需要执行事务提交方法。
- 增删改操作需要执行事务提交方法。
创建/连接数据库
py
#!/usr/bin/python
# 导入 sqlite3 库
import sqlite3
# 如果当前目录没有test.db文件,否则会在当前目录创建test.db文件。
# 然后程序连接test.db文件中的main数据库,并返回一个数据库连接对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
print ("数据库打开成功")sqlite3.connect 方法会在当前目录中,创建一个db文件。并且python会连接到这个db文件中的main数据库,并返回一个数据库连接对象。
数据库连接对象conn中包含了以下方法
- conn.cursor() 创建一个游标对象
- conn.commit() 处理事务提交
- conn.rollback() 处理事务回滚
- conn.close() 关闭一个数据库连接
创建/连接数据库的其他写法
py
# 在一个绝对路径下,创建或打开数据库
conn = sqlite3.connect("C:\\Test.db")
# 或者在内存中创建一个数据库
conn = sqlite3.connect("memory")创建游标
游标对象有以下方法支持数据库操作。
py
# 创建游标对象
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 用来执行sql语句
cursor.execute()
# 用来执行多条sql语句
cursor.executemany()
# 用来关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 用来从结果中取一条记录,并将游标指向下一条记录
cursor.fetchone()
# 用来从结果中取多条记录。
cursor.fetchmany()
# 用来从结果中取出所以记录。
cursor.fetchall()
# 用于游标滚动。
cursor.scroll()创建表
下面的代码,它会在 test.db 的main数据库中创建 t_user 表,
py
#!/usr/bin/python
import sqlite3
# 连接test.db文件,并返回一个数据库对象
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
print ("数据库打开成功")
# 创建一个游标对象
c = conn.cursor()
sql = '''
CREATE TABLE t_user(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL AUTOINCREMENT,
NAME TEXT NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
ADDRESS CHAR(50) ,
region TEXT NOT NULL DEFAULT 'null', --地区
);'''
# 游标执行SQL语句
c.execute(sql)
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
print ("数据表创建成功")
# 关闭数据库连接
conn.close()- connection.cursor 方法会创建一个游标对象,游标对象用于执行SQL语句。
- cursor.execute方法用于执行SQL语句。
- connection.commit() 方法会提交当前的事务。如果未调用该方法,那么自上一次调用 commit() 以来所做的任何数据库操作对数据库连接来说是不可见的。
- connection.close() 该方法关闭数据库连接。请注意,这不会自动调用 commit()。如果您之前未调用 commit() 方法,就直接关闭数据库连接,您所做的所有更改将全部丢失。
INSERT 操作
向t_user表中插入多条数据。
py
#!/usr/bin/python
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
c = conn.cursor()
print ("数据库打开成功")
c.execute("INSERT INTO t_user (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS) \
VALUES (1, 'Paul', 32, 'California')")
c.execute("INSERT INTO t_user (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS) \
VALUES (2, 'Allen', 25, 'Texas')")
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
print ("数据插入成功")
# 关闭数据库连接
conn.close()- cursor.execute方法用于执行SQL语句。该SQL语句中可以使用占位符代替 SQL 文本。
SELECT 操作
查询操作不需要提交。非查询操作才需要提交
py
#!/usr/bin/python
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
c = conn.cursor()
print ("数据库打开成功")
sql = "SELECT id, name, address from t_user"
results = c.execute(sql)
list_data = results.fetchall()
for row in list_data:
print("ID = ", row[0])
print("NAME = ", row[1])
print("ADDRESS = ", row[2])
print ("数据操作成功")
conn.close()- fetchall() 获取结果集中所有(剩余)的行,返回一个列表。当没有可用的行时,则返回一个空的列表。
UPDATE 操作
py
#!/usr/bin/python
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
c = conn.cursor()
print ("数据库打开成功")
# 执行语句
c.execute("UPDATE t_user set address = 'beijing' where ID=1")
# 提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()DELETE 操作
py
#!/usr/bin/python
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.connect('test.db')
c = conn.cursor()
print ("数据库打开成功")
c.execute("DELETE from t_user where ID = 2;")
# 提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()python 操作sqlite3模块 返回字典形式的查询结果
当我们使用python执行查询语句的时候,查询结果有可能是元组的形式。通常情况下我们会将元组类型的查询结果,转换为字典类型。
解决办法:需要先进行配置
py
import sqlite3
# 该方法将元组转化为字典
def dict_factory(cursor, row):
d = {}
for idx, col in enumerate(cursor.description):
d[col[0]] = row[idx]
return d
con = sqlite3.connect("test.db")
# 设置row_factory
con.row_factory = dict_factory
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "SELECT * FROM t_user"
results = cursor.execute(sql)
list_data = results.fetchall()
print("查询结果列表为:",list_data)判断表是否存在
py
import sqlite3
# 判断表是否存在
def isExistTable(tableName):
conn = sqlite3.connect("test.db")
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = f"SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type='table' AND name='{tableName}';"
results = cursor.execute(sql).fetchall()
if len(results) == 0:
return False
else:
return True
# 测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = isExistTable('t_job_info')
print(a)